Hypoparathyroidism types: How do they differ?
Last updated June 4, 2025, by Marisa Wexler, MS

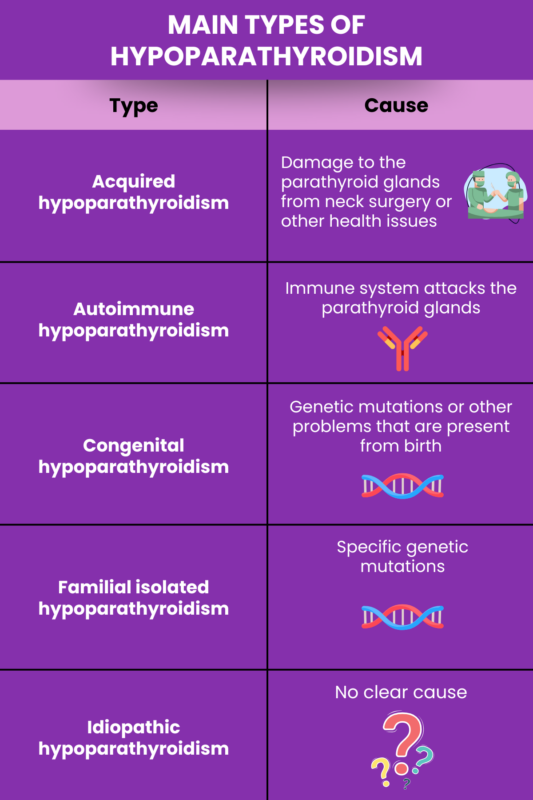
There are several types of hypoparathyroidism, the main ones being acquired, autoimmune, congenital, familial isolated, and idiopathic hypoparathyroidism.
All types are marked by abnormally low levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH) — a signaling molecule that helps regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in the body — due to reduced function or damage to the parathyroid glands, small glands located in the neck.
However, each type is defined by a distinct underlying cause and requires a different management approach, so accurately determining a person’s disease type is essential for proper treatment.
Main types of hypoparathyroidism
In hypoparathyroidism, low PTH levels cause the body’s calcium-phosphorus balance to become disrupted, ultimately leading to disease symptoms such as muscle cramps, brain fog, fatigue, or chronic kidney disease.
Because all hypoparathyroidism types are marked by low PTH levels, disease manifestations and symptoms are generally similar across types — but the underlying cause of low PTH levels differs.
Across all forms of hypoparathyroidism, the main goal of treatment is to normalize calcium levels, as most hypoparathyroidism symptoms actually arise due to abnormal calcium levels.
This is usually done by taking supplements of calcium and vitamin D, which helps the body absorb calcium. Additional treatments may also be needed if supplements are insufficient to control symptoms or if other health problems are present in addition to hypoparathyroidism.
Acquired hypoparathyroidism
Acquired hypoparathyroidism is the most common form of the disease. It occurs when healthy parathyroid glands become damaged during a person’s lifetime and can no longer produce adequate amounts of PTH.
Common causes of parathyroid damage that can lead to acquired hypoparathyroidism include:
- injury due to neck or thyroid surgery (the most common cause, accounting for about 75% of all hypoparathyroidism cases)
- high levels of copper or iron
- low magnesium levels
- cancer that spreads to the parathyroid glands
- radiation therapy to the neck.
Acquired hypoparathyroidism symptoms are typically similar to those of other forms and include muscle cramps or abnormal sensations. However, the disease’s severity and exact manifestations can vary from person to person.
Autoimmune hypoparathyroidism
Autoimmune hypoparathyroidism, the second most common form of the disease, develops when the immune system mistakenly attacks the parathyroid glands, causing damage that results in insufficient PTH production.
This type often co-occurs with other autoimmune diseases. As a result, autoimmune hypoparathyroidism symptoms may also include features of these overlapping autoimmune conditions in addition to the classic symptoms of the disease.
Congenital hypoparathyroidism
The word congenital means “present at birth.” As such, congenital hypoparathyroidism is a form of the disease that is present when someone is born. It can sometimes occur due to developmental defects that affect the parathyroid glands, or it may result from genetic mutations.
Several inherited syndromes or diseases are known to cause this form of the disease, including:
- polyglandular autoimmune syndrome type 1 (caused by mutations in the AIRE gene). Because it is marked by autoimmune disease, it is also sometimes classified as a form of autoimmune hypoparathyroidism.
- DiGeorge syndrome (caused by mutations in the TBX1 gene)
- hypoparathyroidism-retardation-dysmorphism syndrome (caused by mutations in the TBCE gene)
- hypoparathyroidism-deafness-renal dysplasia syndrome, also called Barakat syndrome (caused by mutations in the GATA3 gene)
- Kenny-Caffey syndrome (caused by mutations in the FAM111A gene)
- Kearns-Sayre syndrome, mitochondrial encephalopathy, and mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency syndrome (caused by mutations in genes that affect mitochondria, cellular structures used for energy production).
Congenital hypoparathyroidism symptoms vary depending on the specific underlying cause. Because some associated syndromes also lead to issues with other organs or tissues, patients may experience symptoms that go beyond the classic symptoms caused by damage to the parathyroid glands.
Familial isolated hypoparathyroidism
Familial isolated hypoparathyroidism, sometimes abbreviated FIH, is a group of genetic disorders in which patients have low PTH levels without other associated health issues.
It is usually caused by mutations in genes that directly or indirectly control PTH production and secretion in the parathyroid glands, including:
- PTH
- GCM2
- GNA11
- CASR
- SOX3.
Familial isolated hypoparathyroidism symptoms usually begin in childhood, though they may not become apparent until adolescence or adulthood in some patients. Seizures during infancy or childhood are sometimes the first sign of the disease.
Idiopathic hypoparathyroidism
The word idiopathic means “of unknown origin.” As such, idiopathic hypoparathyroidism refers to a form of the disease where the underlying cause is unknown.
The diagnosis is made when a person has low PTH levels but clinicians are not able to pinpoint a genetic, autoimmune, or acquired cause, and there is no family history of the disease.
As patients also have low PTH, idiopathic hypoparathyroidism symptoms are generally similar to those seen in other forms of hypoparathyroidism and are mostly related to calcium deficiency.
Primary vs. secondary hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism is sometimes classified as either primary hypoparathyroidism or secondary hypoparathyroidism, depending on the origin of the problem.
Some sources suggest that primary hypoparathyroidism develops due to defects within the parathyroid glands, mainly from genetic causes, while secondary hypoparathyroidism arises from other causes that impair the function of the parathyroid glands. Based on these definitions, congenital or familial isolated hypoparathyroidism could be considered primary forms of the disease, while secondary hypoparathyroidism, a much more common form, could include cases arising from copper excess or autoimmune diseases.
However, definitions of primary versus secondary hypoparathyroidism can vary across studies. There is also no clear consensus in the scientific literature about how specific types of hypoparathyroidism should be classified, with distinct sources categorizing the same condition in different ways.
Hypoparathyroidism News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Recent Posts
- With hypoparathyroidism, it helps to find the right calcium supplement
- Parathyroid gland transplant foils permanent hypoparathyroidism
- Considering language, ritual, and the way I speak my truth
- Reframing my hypoparathyroidism diagnosis anniversary
- A supportive family helps me navigate life’s twists and turns
Related articles
-
July 4, 2025 by Heather Novak
Reframing my hypoparathyroidism diagnosis anniversary
-
June 27, 2025 by Heather Novak
How to deal with heat when living with hypoparathyroidism